Surgical Excision of Melanoma
Surgery Overview
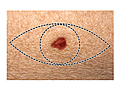
Surgery to remove (excise) a melanoma removes the entire melanoma along with a border (margin) of normal-appearing skin. The width of the border of normal skin removed depends on the depth of the melanoma. More tissue, usually skin and fat, is also removed from under the melanoma.
- Small excisions may be closed with stitches and heal without problems.
- Large excisions or those located on the hands, face, or feet may require a skin graft to close the wound after surgery.
The type of anesthetic used for your surgery depends on the size and location of the melanoma. Surgery on small, easily reached melanomas may require only a local anesthetic, while surgery for larger melanomas may require general anesthesia.
What To Expect
Recovery after surgery to remove a melanoma depends upon the site and extent of surgery. The wound may take longer to heal if reconstructive surgery techniques such as skin grafts are used.
Why It Is Done
Surgery is the most common treatment for melanoma. Sometimes lymph nodes may be removed at the same time to check them for cancer. Surgery also may be done to remove lymph nodes that have cancer or to remove tumors that may have spread to other parts of the body.
How Well It Works
Surgery to remove the melanoma usually cures melanoma if it is found early. Surgery may cure melanoma if the cancer is only in the nearby lymph nodes.
Surgery may be used to treat metastatic melanoma. This only cures the cancer in a few cases. But surgery may provide the most effective and longest-lasting relief of symptoms.
Risks
Risks of surgery to remove melanoma include:
- Infection.
- Scarring.
- Bleeding.
- Rejection of skin graft.
What To Think About
Your doctor may need to do a biopsy (sentinel lymph node biopsy) of the lymph nodes near the melanoma to see if the cancer has spread (metastasized). The biopsy will be done before or during surgery to remove the melanoma.
Credits
Current as of: December 19, 2018
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:Kathleen Romito, MD – Family Medicine & Amy McMichael, MD – Dermatology
Current as of: December 19, 2018
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:Kathleen Romito, MD – Family Medicine & Amy McMichael, MD – Dermatology
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Learn how we develop our content.