Personal Health Records
Larry Weed, an American physician and researcher, put forth the idea of electronically recording patients’ medical history & data over 50 years ago.
The importance of medical records, captured by both patient and physician, can’t be underestimated in today’s data-driven healthcare world. Whether the handwritten Covid shot information card from your latest booster shot or your Apple Watch data that captures your heart rate, the amount of patient-volunteered and controlled health data is exploding. It’s not the same as the data from a hospital or doctor, but can play a vital role in properly managing your own healthcare.
Let’s take a deep dive into the many aspects of personal health records, how it is different from electronic records and patient portals, and learn about the top PHR software for 2022.
What are Personal Health Records?
PHR is an electronic documentation of an individual’s health information that can be managed, edited, and tracked by them or someone they authorize. Written from a patient’s perspective, it contains a list of all medical conditions, medications, and treatments with additional information, such as allergies or family history.
You are probably already using a PHR if you’re keeping track of your medical records inside a folder, and you may know the big load of paper they bring, which makes it challenging to have crucial data at your fingertips.
The idea of a personal health record is to have all your health information in one place for quick access whenever you need it. For using the PHR successfully, it’s essential that you actively update any change in your health and medical situation and share them with your doctor or healthcare providers.
Note: Unlike electronic medical records (EMRs), personal health records can be used without care providers’ involvement since these are not considered part of regular medical records.
What is in a PHR?
A PHR contains any information that helps your doctor make informed decisions regarding your health & treatments.
- Name & contact info of healthcare provider or doctors
- Allergies, including food or drug allergies
- Medications
- Past surgeries and any medical conditions
- Chronic health problems like diabetes & high blood pressure
- Family history
- Immunization details
- Blood Tests & Lab reports
- Diet, workout habits, and health goals if you wish to add these
What are the Types of Personal Health Records?
According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, there are two broad categories of personal health records:
- PHRs Offered by HIPAA Covered Entities
- PHRs Not Offered by HIPAA Covered Entities
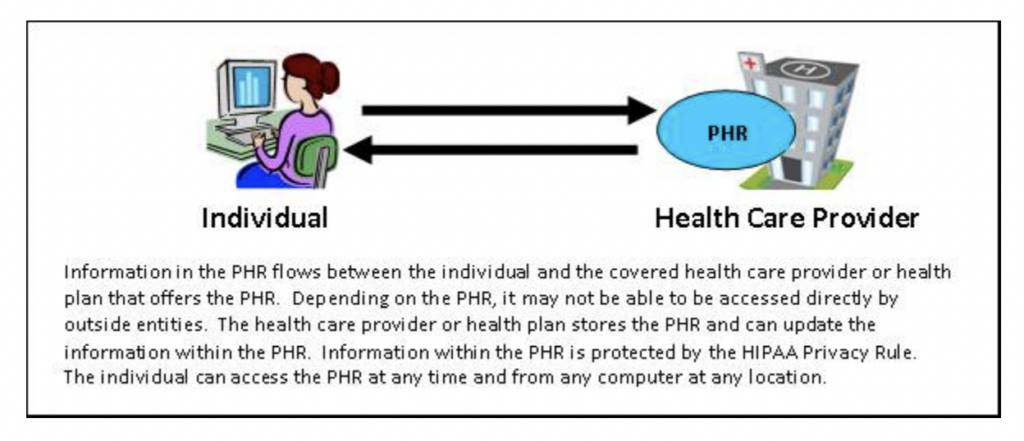
PHRs Offered by HIPAA Covered Entities
When a healthcare provider or health plan that falls under HIPAA offers a PHR, it is subject to the Privacy Rule. In these cases, the individual can view either the entire or partial record and is generally linked to them within the HIPAA-covered entity.
Source: HSS Govt
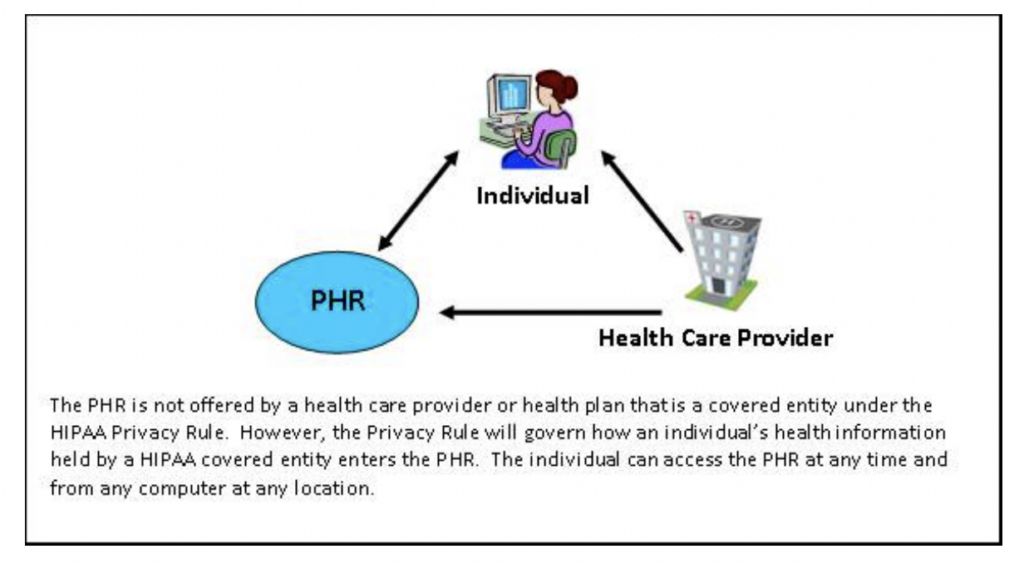
PHRs Not Offered by HIPAA Covered Entities
The Privacy Rule does not apply to PHRs that are not offered by health plans or providers covered by HIPAA. A great example includes records offered by employers or by a PHR vendor directly to an individual. In this case, the PHR is subject to the privacy rules of the entity instead.
Source: HSS Govt
PHRs can also be categorized as:
- Maintained by patients (Untethered)
- Recorded by Healthcare entities (Tethered)
The PHRs maintained by patients or individuals are standalone and are shared only with the people or entities they give consent to. It contains information populated by the individual, either independently or after collecting from various healthcare sources. On the other hand, the PHRs maintained by healthcare providers are linked to their electronic health record (EHR) system and can be accessed through a patient portal. Depending on the kind of data, the individuals can view either the entire record or part of it.
What are the Benefits of a Personal Health Record?
In a PHR, you can keep track of what kind of medications you are taking, when and how much, and which ones cause adverse effects. You can also keep track of your results in physical examinations and any other tests or diagnoses.
While it could be a hassle to keep your PHR up-to-date, the benefits it brings are multifold.
- PHRs are the first tool you can use in an emergency, as it contains information that can be given to first aid providers.
- When consulting different specialists & healthcare providers, patients can collect data stored in other EHR systems, cumulate it, and gather it in one place.
- PHRs make it easy for caregivers to access, manage, and utilize the entire family’s healthcare information more efficiently.
- PHRs make it easy for doctors & other medical professionals to make well-informed decisions regarding a patient, especially in a time-critical emergency.
What is a Patient Portal?
A patient portal is defined as a secure website that helps patients access their health information online, round the clock. A patient can log in with secure credentials, access information confidentially, and sometimes even communicate with their healthcare provider, book appointments, or make payments.
Some of the data a patient portal provides are:
- Records of hospitalization & Discharge summaries
- Allergies
- Immunization
- Lab Results
- Any medical conditions or diseases
- Consultations with doctors & medical professionals
- Surgeries or procedures performed
PHRs Vs Patient Portals
A personal health record and patient portal essentially serve the same purpose- they help patients access crucial health information & medical history quickly. While a patient portal is controlled by a healthcare entity such as a hospital, a PHR is generally managed by the individual, their family, or any party they have given access to.
What are EMRs & EHRs?
EMR (Electronic Medical Record) refers to a digital version of a single chart containing a patient’s information. On the other hand, EHR (electronic health record) is a more comprehensive digital document that includes the entire health history & medical info of a patient.
You can find both the terms used interchangeably; however, they aren’t the same. EMRs typically stay between the organization & patient. On the contrary, EHR systems are built for interoperability; in this manner, when a patient switches healthcare providers, the data gets transferred in real-time, saving much hassle. They are also designed for easy sharing between authorized healthcare providers & entities.
PHR Vs EMR Vs EHR
An individual maintains a PHR for their record-keeping and reference. It can be shared with family or any entities with consent. In addition, it also contains info that helps the individual with their personal health goals.
EMR refers to a document containing all health info of a patient of a single practice. Healthcare providers mainly use it for their internal purposes and can be shared with the patient upon request.
EHR refers to a more comprehensive record that documents the entire health & medical history of a patient and is updated whenever a new visit, consultation, or procedure is done. Moreover, it can be shared with other healthcare entities when patients change doctors or healthcare treatments.
List of 40 Personal Health Record Software in 2022
Software in the field of medication helps the exchange of information electronically, providing a high-quality and safe service for patients while enhancing Companies’ efficiency.
- Accurate and up-to-date patient information
- Efficiency in care and management of patients
- Fast access to information and medical records for patients
- Safe sharing of information between patients and professionals
- Improvement of the quality of communication between patients and doctors
- Safe prescriptions
- Electronic compiled documentation, available whenever needed and legible
- Enhanced privacy for patients
- Less paper and fewer costs
Overall, those software enables a different culture in the relation of patients, hospitals, and medical professionals in general, transforming health care step by step: improvement of safety, efficiency, effectiveness, equity, and patient-centeredness. Let’s see some of the PHR software in the market for 2022.
-
Access My Health
Access My Health is a cloud-based PHR service for health, medical, and legal records. This PHR offers a medical ID card, prescription discount cards, an ICE program, an online blood lab, medical ID bracelets, a health information library, and a pharmacy locator.
-
American Medical ID
American Medical ID allows you to maintain an online personal health file of your medical records and sells medical jewelry so your medical personnel can be informed of your medical conditions.
-
Care Medical History Bracelet
Care Medical History Bracelet sells emergency bracelets that can be plugged into any computer, providing instant access to your complete health history along with e-Manager Software.
-
GlobalPatientRecord
GlobalPatientRecord is a personal health record for you and your loved ones. This PHR offers you constant online access to your health information, interaction with your healthcare provider online, and health reminders.
-
Health Companion
is a healthcare social network that serves as a PHR. This PHR allows you to control and organize your healthcare records, track your prevention and wellness, and communicate with your health providers.
-
Health String
Health String is an online wellness program that allows you to live a healthier life. The way the program works is individuals are paired with a registered nurse, who will create a personalized wellness strategy for them.
-
Health Vault
Health Vault is Microsoft’s platform for people to gather, store, use, and share health information online. The three pillars of Health Vault are organization of your family’s medical data, preparation for doctor’s appointments and unexpected emergencies, and a comprehensive look into your health in one place.
-
HealtheTracks
HealtheTracks is an affordable online PHR system for the whole family which you can try with a free trial. HealtheTracks PHR offers many categories, ranging from Children’s Healthy Check Ups to Dental Records.
-
Innovision Corp
Check Up, Innovision Corp’s software, helps parents keep track of their children’s immunizations, athletes record their diet and workout, and someone fighting cancer documents their prescriptions and doctor’s appointments.
-
Kare Information Services
Kare Information Services (KIS) offers a personalized medical records profile that is accessible online 24/7.
-
Life On Key
The Lynx Healthcare Navigator will help you get the most effective care from your physician and give you full control over your medical records. This program offers condition-specific health and wellness tools.
-
Life Saver App
LifeSave App provides a medical ID card that gives you and medical professionals access to your medical records online. This application is vital for individuals with chronic illness, caregivers, home health care professionals, etc.
-
LifeLedger
LifeLedger is a PHR for adult children to assist their aging parents with options of a free or premium account.
-
MedCommons
MedCommons is an online venue to transfer medical images for patients. This service allows you to upload pictures from either a CD or scanner for free for 40 uploads per month.
-
MedDataNet.com
MedDataNet.com sells patented bracelets and pendants that are encoded with a personalized code that gives either them or medical professionals access to their medical records online.
-
Medefile
Medefile is a trusted service that collects, organizes, and stores medical records. This online service allows you to upload the medical images straight from a CD or scanner for free for up to 40 transfers per month.
-
Medic Alert Foundation
Medic Alert Foundation offers medical IDs in the form of jewelry to be able to alert medic responders to underlying medical conditions. This program offers many different types of MedicAlert memberships to find your personal health needs.
-
MedNotice
MedNotice provides secure storage for your medical records and an ID card for your wallet. Your PIN number is located on your ID card to ensure that any health professional will be able to access necessary medical information in the case of an emergency.
-
My Family Health
The Surgeon General’s Office provides MyFamily Health, which stores your family health history and allows you to print and share the information. This service is also available in multiple languages, including Spanish, Portuguese, and Italian.
-
My Vet Health
My Vet Health is the online personal medical records system for VA patients. This PHR was specifically designed for Veterans, active duty Servicemembers, their dependents, and caregivers.
-
MyHealthFolders.com
MyHealthFolders offers secure web-based health information management and emergency access to your health information by health professionals.
-
MyMedicalrecords.com
MyMedicalRecords.com offers multilingual personal health records and electronic safe deposit box storage solutions. This PHR is key for taking control of your health.
-
MyMedLab
MyMedLab is a platform of all resources regarding medical laboratory testing that is centralized around their personal medical records system.
-
MyPHR
MyPHR offers medical record storage perfect for parents, seniors, chronically ill, and caregivers. MyPHR is the perfect resource for seniors, parents, those who are chronically ill, and caregivers.
-
NoMoreClipboard
NoMoreClipboard provides consumers with a portable, patient-managed personal health records platform. This PHR is ideal for individuals with a chronic conditions, baby boomers who find themselves taking care of aging relatives, older children and their own health care needs, or aging seniors.
-
Partners Healthcare
Patient Gateway offers a secure electronic link between you and your doctor. This resource is a venue to request routine appointments, prescriptions, and referrals.
-
Patient Ally
Patient Ally is a time-saving personal health record management system. Patient Ally keeps track of your health data for free while also allowing you to connect to your doctor to schedule/change appointments and request medicine or prescriptions.
-
Patient Fusion
Patient Fusion offers quick access to your health records in conjunction with your doctor. Use this mobile application on the go so you’re never without your medical information anywhere in the world.
-
Patients Like Me
Patients Like Me is a real-time health information sharing website for patients, including personal stories and health data about your condition. This website includes a personalized health tracker.
-
People Chart
People Chart provides a service that helps patients gather and use their medical records to improve their health care at home and while traveling.
-
Records For Living
Health Frame, Records For Living’s program, consolidates all of your family’s medical records in an organized fashion. Use this vital resource to stay on top of doctors’ appointments and prepare for unexpected emergencies.
-
Tolven Health
Tolven offers a healthcare informatics platform, an electronic clinician and personal health record, and a health analytics solution.
-
Wakefield Soft
Health File is a personal medical record and information organization software for your mobile devices, such as Palm OS, Pocket PC, and Windows Mobile.
-
Web MD Manager
WedMD Manager offers personal and family health records storage and emergency health cards for your wallet.WebMD is a renowned healthcare website and its PHR has excellent reviews.
-
Zebra Health
Zebra Health gives you control of your healthcare by offering free personal health records online. This PHR gives you more control over your health.