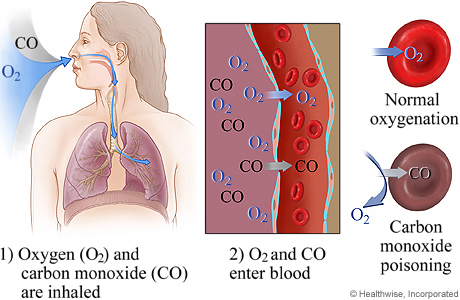
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Current as of: December 13, 2018
Author: Healthwise Staff
Medical Review:Anne C. Poinier, MD – Internal Medicine & Kathleen Romito, MD – Family Medicine & Adam Husney, MD – Family Medicine & R. Steven Tharratt, MD, FACP, FCCP – Pulmonology, Critical Care Medicine